Scientists have extensively studied Omega-3 for its potential health benefits and its role in fitness goals. But what exactly is Omega-3, and does the research support its reputation? In this article, we’ll explore what Omega-3 is, its health advantages, its potential impact on your workouts, and the recommended safe dosage.

What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats that contribute to overall health and well-being. Commonly known as “good fats,” they are found in foods like fish, nuts, and seeds. These fats play a key role in maintaining heart, brain, and joint health.¹²Omega-3 fatty acids are healthy fats that our bodies need but can’t produce on their own.
What is omega-3?
Omega-3 is a type of polyunsaturated fat, and is classified as an essential fatty acid, meaning that it has to be sourced from our diets as it cannot be produced by our bodies.8
Omega-3 comes in many different forms that vary in both length and chemical structure. There are short-chain omega-3 fatty acids which can come from plant-based sources such as leafy green vegetables, walnuts, and flaxseed. If you see the name ALA or alpha-linolenic acid, this is a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid.8
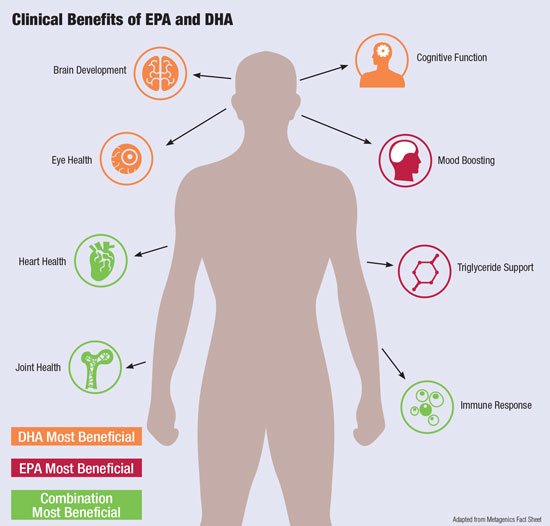
Long-chain fatty acids are the other common form of omega-3. These omega-3 fatty acids contain eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). EPA and DHA are linked to brain and eye health and are important structural components of cells in the body.13 They’re naturally found in algae, which are eaten by fish and other sea life. These fatty acids are often referred to as marine-source omega-3, or fish oils.8
It’s worth noting that the body doesn’t absorb both sources of omega-3 in the same way. Our metabolism can only convert around 5% of plant-based ALA omega-3 into EPA, so this is worth keeping in mind when considering which type to go for, as well as dosage. 8
What is the difference between fish oil and omega-3?
Fish oil and Omega-3 are often confused, but they’re not the same.
Omega-3 is an essential fatty acid that the body needs but can’t produce on its own, so it must come from food or supplements.
Fish oil is a supplement made from oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. It’s packed with EPA and DHA, two types of Omega-3 that help reduce inflammation, support brain function, and promote heart health.³⁴⁵
However, fish oil isn’t the only way to get Omega-3. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, algae, and plant oils like rapeseed and soybean are also good sources.
If you want to boost your Omega-3 intake but don’t like fish oil, algae-based supplements are a great alternative.
What are the three types of omega-3 fatty acids?
There are three main types of Omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
- ALA is a plant-based Omega-3 found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Since the body can’t produce it, we must get it from food. While ALA can convert into EPA and DHA, this process is not very efficient.⁶
- EPA and DHA are mostly found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. They are known for their anti-inflammatory benefits and overall health support. DHA is especially important for brain and eye health, making it crucial for pregnant women and young children.⁷
Sources of omega-3
Here are some excellent sources of Omega-3:
- Fatty Fish – Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are rich in Omega-3, along with vitamin D, selenium, and high-quality protein.
- Flaxseeds – These tiny seeds are packed with Omega-3. Sprinkle them on cereal, yogurt, or blend them into smoothies.
- Chia Seeds – Another great plant-based source of Omega-3. Add them to oatmeal, baked goods, or make chia pudding.
- Walnuts – A crunchy, nutritious snack that’s high in Omega-3. Enjoy them on their own or mix them into salads, oatmeal, or baked treats.
- Hemp Seeds – These nutty-flavored seeds are growing in popularity as an Omega-3 source. Sprinkle them on salads, smoothies, or roasted veggies.

Omega-3 health benefits
Omega-3, particularly from fish oil, is often linked to various health benefits—but what does the science say? Let’s explore some of the key benefits of Omega-3:
Fish oil and insulin sensitivity
Fish oils have been thought of by many health practitioners to help reduce blood pressure and therefore lower cardiovascular risk. A study has investigated these claims, alongside scientific evidence, and found that fish oils showed a very modest, real-life effect. The study determined that there was an effect of fish oils on blood pressure, and ruled out the possibility of pure chance. 3
There can be no argument that any reduction in high blood pressure is a good thing, but not at the expense of blood pressure medication. If you’re using blood pressure medication to treat high blood pressure, then it’s recommended to consult a medical professional before considering using or switching to fish oils to help further reduce your risk.
Supports your immune system
Omega-3 plays a vital role in supporting the immune system by providing the nutrients it needs to fight infections and diseases.
One key way it helps is by reducing inflammation. While inflammation is a natural response when the body is healing, chronic inflammation can weaken the immune system over time. Omega-3’s anti-inflammatory properties help regulate this process, ensuring the immune system focuses on fighting germs instead of being overwhelmed by excess inflammation.
Omega-3 also boosts the function of immune cells. It enhances the activity of white blood cells, which are responsible for identifying and attacking foreign invaders in the body.
Moreover, Omega-3 supports the production and activity of important immune molecules like cytokines and antibodies, which are essential for coordinating the immune response and battling infections. By optimizing the performance of these cells, Omega-3 helps strengthen the immune system’s ability to protect the body.
Promotes a healthy heart
Omega-3 fatty acids are good for a healthy heart. They have been shown to improve overall cardiovascular health.4
One of the main ways omega-3s benefit the heart is by reducing inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to poor heart health, and omega-3s help to counteract it.
Omega-3s have also been found to lower blood pressure and triglyceride levels, both of which are risk factors for heart disease.
By incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet or taking supplements, you can help keep your heart healthy and strong.
Improves bone and joint health
Omega-3 fatty acids have a significant impact on the strength and flexibility of bones and joints. By reducing inflammation, a major contributor to conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis, Omega-3-rich foods or supplements can help manage the symptoms of these conditions.²⁹
Omega-3s may also support bone and joint health by improving calcium absorption. Calcium is essential for strong bones, but it needs to be properly absorbed to be effective. Since calcium absorption decreases with age, Omega-3 is especially important for older individuals.
Additionally, studies show that Omega-3s help promote bone formation and enhance bone density, both of which are crucial for maintaining strong, healthy bones and joints.⁹
A better night’s sleep
Omega-3s have been shown to help regulate hormones that play a role in sleep. For instance, they can influence the production of melatonin, a hormone that controls the sleep-wake cycle. By regulating melatonin, Omega-3s can help improve the quality of your sleep.
Omega-3s also assist in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that affects both mood and sleep. By boosting serotonin levels in the brain, Omega-3 can promote a more balanced sleep-wake cycle, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Additionally, Omega-3s’ anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce the symptoms of certain sleep disorders, like sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome, both of which can disrupt sleep and cause fatigue.
By adding Omega-3-rich foods to your diet or taking a high-quality Omega-3 supplement, you may be able to alleviate some of these sleep issues and enjoy a better night’s rest.
Promotes healthy skin
While many skincare products claim to offer miraculous results, the secret to healthier skin may be in your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids are known to provide a range of benefits for skin health.
Omega-3 helps maintain the integrity of cell membranes, which is essential for keeping the skin hydrated and protected from external damage. By nourishing skin cells from the inside, Omega-3 can reduce inflammation, minimize redness, and even improve conditions like eczema and psoriasis.¹³
Additionally, Omega-3 boosts collagen production, the protein responsible for maintaining skin’s elasticity and firmness. As we age, collagen levels decrease, leading to wrinkles and sagging. By adding Omega-3-rich foods to your diet or taking supplements, you can help stimulate collagen production and improve your skin’s overall appearance.
Omega-3s also have antioxidant properties, helping protect your skin from free radicals—unstable molecules that damage cells and speed up aging. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, Omega-3 helps promote a healthier, more youthful complexion.
Reaching fitness goals with Omega-3?
Omega-3 and fat loss
It might seem surprising that consuming fat can help with fat loss, but Omega-3s are different. These fatty acids have been shown to increase metabolism, enhance the body’s ability to burn calories, and even reduce appetite.¹⁴¹⁵
One key reason Omega-3s aid fat loss is by helping regulate leptin, the hormone responsible for controlling hunger and signaling fullness to the brain. Without enough Omega-3s, leptin levels can become imbalanced, leading to increased hunger and overeating. By adding Omega-3-rich foods or supplements to your diet, you can help keep leptin levels stable, reducing the risk of overeating and supporting fat loss.
Omega-3s also help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to obesity and metabolic disorders.¹⁶ By lowering inflammation, Omega-3s support a healthier metabolism, which can assist in fat loss.
Additionally, Omega-3s improve insulin sensitivity. Insulin regulates blood sugar levels and plays a key role in metabolism. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it can cause weight gain and difficulty losing fat. Omega-3s improve insulin sensitivity, helping your body use glucose for energy rather than storing it as fat.
Omega-3 and muscle gain
When it comes to building muscle, most people focus on protein, but Omega-3 fatty acids also play an important role in muscle growth.¹⁷
One way Omega-3s support muscle gain is by reducing inflammation after intense workouts. Excessive inflammation can slow down muscle recovery and hinder growth, but Omega-3’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce this, allowing for faster recovery and better muscle development.
Omega-3s also improve blood flow to the muscles, delivering more oxygen and nutrients needed for muscle repair and growth.
Furthermore, Omega-3s enhance protein synthesis, the process by which the body builds new proteins. By boosting protein synthesis, Omega-3s can help increase muscle tissue growth, which is particularly beneficial for those involved in strength training or resistance exercises.
Omega-3 supplements
Supplements should always be just that — a supplement to your diet, not a replacement. Whether you need to take omega-3 supplements depends on your eating habits. For example, if you follow a plant-based diet, you’ll likely need to get omega-3 from high-quality plant-based sources, since fish or krill oils aren’t suitable. A supplement can help ensure you’re getting the right amount of omega-3.
Even if you’re not vegetarian or vegan, you may wonder whether it’s better to get omega-3 from oily fish or from supplements. While supplements make it easier to consume larger quantities of omega-3, both options—eating oily fish or taking omega-3 supplements—can provide the same benefits.
If you’re in a calorie deficit (eating fewer calories to lose weight), you might miss out on essential nutrients. This could be a good time to consider an omega-3 supplement. It allows you to get enough omega-3 without adding extra calories to your daily intake.
Omega-3 dosage
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to the ideal dosage of omega-3s, but a typical recommendation is around 250-500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA (the two main types of omega-3s found in fish oil) per day.¹⁴ However, for individuals with specific health concerns, higher doses may be recommended.
If you’re getting your omega-3s from food, the general guideline is to have two servings of fatty fish (like salmon, mackerel, or sardines) each week. This can help meet your omega-3 needs.
If you don’t eat fish or have dietary restrictions, omega-3 supplements can be an easy alternative. When selecting a supplement, look for one that provides at least 500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA per serving.
It’s also essential to pay attention to the quality of your omega-3 supplement. Choose products that have been tested for purity and potency to ensure you’re getting an effective and reliable product. Always read the label to understand the dosage per capsule and the serving size.
Is it good to take omega-3 every day?
The answer is yes, you can benefit from taking omega-3 supplements!
Many health experts recommend taking omega-3s daily to ensure you’re getting enough of these essential fats. Since your body doesn’t produce omega-3s, it’s important to get them through your diet or supplements. Whether you include them in your meals or take them in capsule form, consistency is key to reaping the full benefits of omega-3s.
However, can you have too much of a good thing? Yes, it’s possible.
While omega-3s are generally safe, excessive intake can lead to some side effects. Extremely high doses can increase the risk of bleeding, especially if you’re on blood-thinning medications. It may also cause gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea or an upset stomach. However, these side effects are rare and typically occur only with very high amounts of omega-3.
Potential side effects of taking omega-3
Omega-3 is generally considered a low-risk supplement when used properly. As long as you don’t replace prescribed medications with fish oils, and stick to the recommended daily dosage, there are typically no issues associated with its use. ¹²





Your blog is a constant source of inspiration for me. Your passion for your subject matter shines through in every post, and it’s clear that you genuinely care about making a positive impact on your readers.